数据结构
一、栈
1.1定义
下压栈(简称栈)是一种基于后进先出(LIFO)策略的集合类型。
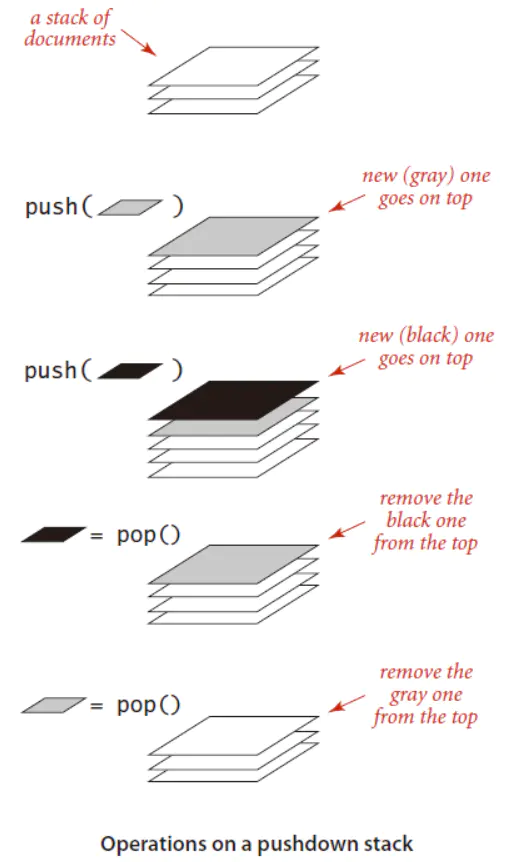
1.2API

1.3实现
1.3.1数组实现
可动态调整大小的栈实现(数组方式):当栈容量满时,采用遍历数组的方式进行扩容,默认调整为原容量的2倍。当栈容量变成1/4时,默认调整为原容量的1/2。
public class ResizingArrayStack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Item[] a; // array of items
private int n; // number of elements on stack
/**
* Initializes an empty stack.
*/
public ResizingArrayStack() {
a = (Item[]) new Object[2];
n = 0;
}
/**
* Is this stack empty?
* @return true if this stack is empty; false otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return n == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of items in the stack.
* @return the number of items in the stack
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
// resize the underlying array holding the elements
private void resize(int capacity) {
assert capacity >= n;
// textbook implementation
Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp[i] = a[i];
}
a = temp;
// alternative implementation
// a = java.util.Arrays.copyOf(a, capacity);
}
/**
* Adds the item to this stack.
* @param item the item to add
*/
public void push(Item item) {
if (n == a.length) resize(2*a.length); // double size of array if necessary
a[n++] = item; // add item
}
/**
* Removes and returns the item most recently added to this stack.
* @return the item most recently added
* @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item pop() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
Item item = a[n-1];
a[n-1] = null; // to avoid loitering
n--;
// shrink size of array if necessary
if (n > 0 && n == a.length/4) resize(a.length/2);
return item;
}
/**
* Returns (but does not remove) the item most recently added to this stack.
* @return the item most recently added to this stack
* @throws java.util.NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
return a[n-1];
}
/**
* Returns an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order.
* @return an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order.
*/
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ReverseArrayIterator();
}
// an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private int i;
public ReverseArrayIterator() {
i = n-1;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return i >= 0;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return a[i--];
}
}
}
1.3.2链表实现
栈的链表实现方式:栈顶即链表的头,入栈相当于“头插法”插入元素。
public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node<Item> first; // top of stack
private int n; // size of the stack
// helper linked list class
private static class Node<Item> {
private Item item;
private Node<Item> next;
}
/**
* Initializes an empty stack.
*/
public Stack() {
first = null;
n = 0;
}
/**
* Returns true if this stack is empty.
*
* @return true if this stack is empty; false otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
/**
* Returns the number of items in this stack.
*
* @return the number of items in this stack
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* Adds the item to this stack.
*
* @param item the item to add
*/
public void push(Item item) {
Node<Item> oldfirst = first;
first = new Node<Item>();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
n++;
}
/**
* Removes and returns the item most recently added to this stack.
*
* @return the item most recently added
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item pop() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
Item item = first.item; // save item to return
first = first.next; // delete first node
n--;
return item; // return the saved item
}
/**
* Returns (but does not remove) the item most recently added to this stack.
*
* @return the item most recently added to this stack
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty
*/
public Item peek() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow");
return first.item;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this stack.
*
* @return the sequence of items in this stack in LIFO order, separated by spaces
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (Item item : this) {
s.append(item);
s.append(' ');
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order.
*
* @return an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order
*/
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new ListIterator<Item>(first);
}
// an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node<Item> current;
public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) {
current = first;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
}
二、二叉搜索数
2.1定义
二叉搜索树的关键字总是以满足二叉搜索数性质的方式来存储:
设x是二叉搜索树中的一个节点。如果y是x左子树中的一个节点,那么y.key<x.key。如果y是右子树中的一个节点,那么y.key>x.key。
二叉搜索树的性值允许我们通过一个简单的递归算法来按序输出二叉搜索树中的所有关键字,这种算法称为中序遍历,类似的有先序、后序遍历。
//伪代码表示中序遍历过程
inorder-tree-walk(x)
if x!=nil
inorder-tree-walk(x.left)
print x.key
inorder-tree-walk(x.right)
2.2查询
//x表示二叉搜索树的根节点,k表示查找的关键值
tree-search(x,k)
if x==nil or k==x.key
return x
if k<x.key
return tree-search(x.left,k)
else return tree-search(y.left,k)
//通过while循环来展开递归,效率会高得多
iterative-tree-search(x,k)
while x!=nil and k!=x.key
if k<x.key
x=x.left
else x=x.right
return x
查询最大关键字元素和最小关键字元素:通过树根沿着left或者right指针查找,直到遇到nil节点,即为最小或者最大值。
2.3插入和删除
插入和删除操作会引起二叉搜索树表示的动态集合的变化。一定要修改数据结构来反映这个变化,但修改要保持二叉搜索树性质得成立。
2.3.1插入
//T表示二叉搜索树,z表示要插入的节点
tree-insert(T,z)
y=nil
x=T.root
while x!=nill
y=x
if z.key<x.key
x=x.left
else x=x.right
z.p=y
if y==nill
T.root=z
else if z.key<y.key
y.left=z
else y.right=z
2.3.2删除
从一颗二叉搜索树T中删除一个结点z的整个策略分为三种基本情况:
①如果z没有孩子节点,直接删除,修改父节点,用nil替换作为孩子节点;
②如果z只有一个孩子,那么将孩子结点提升到父结点即可;
③如果z有两个孩子,需要在右孩子中,找到最小值,保留结点然后删除(情况同①、②),将z节点替换为该最小值节点;
首先定义二叉树结点替换方法:
//T表示二叉搜索树,x表示被替换结点,y表示替换结点
transplant(T,x,y)
if x.p==nil
T.root=y
else if x=x.p.left
x.p.left=y
else x=x.p.right
x.p.right=y
if x.p!=nil
y.p=x.p
//T表示二叉搜索树,z表示要删除得结点
tree-delete(T,z)
//第一种情况
if z.left==nil
transplant(T,z,z,right)
//第二种情况
else if z.right==nil
transplant(T,z,z.left)
//第三种情况
else y=tree-minimum(z.right)
if y.p!=z
transplant(T,y,y.right)
y.right=z.right
y.right.p=y
transplant(T,z,y)
y.left=z.left
y.left.p=y
三、红黑树
3.1定义
红黑树是一颗二叉搜索树,他在每个结点上增加了一个存储位来表示结点得颜色,可以是RED或BLACK。通过对任何一条从根到叶子的简单路径上各个结点的颜色进行约束,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路劲长出2倍,因而是近似于平衡的。
树中每个结点包含5个属性:color、key、left、right和p。如果一个结点没有子节点或父节点,则该结点相应指针属性的值为nil。我们可以把这些nil视为指向二叉搜索树的叶结点的指针(外部结点),而把带有关键字的结点视为树的内部结点。一棵红黑树是满足下面红黑性质的二叉搜索树:
①每个结点或是红色,或是黑色;
②根节点是黑色;
③每个叶节点(nil)是黑色;
④如果一个结点是红色的,则它的两个子结点都是黑色的;
⑤对每个结点,从该节点到所有后代叶结点的简单路劲上,均包含相同数目的黑色结点;
3.2旋转
搜索树操作tree-insert和tree-delete在含n个关键字的红黑树,运行花费时间为O(lgn)。由于这两个操作对树做了修改,可能违反了红黑性质。为了维护这些性质,必须要改变树中某些结点的颜色以及指针结构。
指针结构的改变通过旋转来完成,这是一种保持二叉搜索树性质的局部操作。
左旋以x到y的链为"支轴"进行。它使y成为该子数新的根结点,x成为y的左孩子,y的左孩子成为x的右孩子;右旋同理。

//左旋,T代表树,x代表左旋的结点
left-rotate(T,x)
y=x.right
x.right=y.left
if y.left!=T.nil
y.left.p=x
y.p=x.p
if x.p==T.nil
T.root=y
else if x==x.p.left
x.p.left=y
else x.p.right=y
y.left=x
x.p=y
3.3插入
rb-insert(T,z)
y=T.nil
x=T.root
while x!=T.nil
y=x
if z.key<x.key
x=x.left
else x=x.right
z.p=y
if y==T.nil
T.root=z
else if z.key<y.key
y.left=z
else y.right=z
z.left=T.nil
z.right=T.nil
z.color=RED
rb-insert-fixup(T,z)
//每次插入的结点都设置为red,因为红色结点的子节点必须是黑色,所以需要检查父节点颜色
rb-insert-fixup(T,z)
while z.p.color==Red
if z.p==z.p.p.left
y=z.p.p.right
//case1:如果父节点的兄弟结点是红色,则修改父节点及兄弟结点为黑色,父父结点为红色
if y.color==Red
z.p.color=Black
y.color=Black
z.p.p.color=Red
z=z.p.p
//case2:如果父节点的兄弟结点是黑色,父结点为右子结点,则持有父节点,然后进行左旋
else if z==z.p.right
z=z.p
left-rotate(T,z)
//case3:如果父节点的兄弟结点是红色,父节点是左子节点,则持有父父节点,然后进行右旋
else z.p.color=Black
z.p.p.color=Red
right-rotate(T,z.p.p)
else (same as then clause with "right" and "left" exchanged)
T.root.color=Black